Introduction to Cluster Computing
Contents
Introduction to Cluster Computing
Cluster Computing topic is a deep research topic in computer networking. In this article, I will explain to you about Cluster Computing introduction. What supercomputer is. About the motivation of using clusters. CPU cycle stealing. And the concept of cluster-based computing etc. You will get a brief idea on all these topics.
Super Computer in Cluster Computing
Super Computers are exactly computers with superpowers. They are high in performance. IBM Roadrunner is one of the powerful super computers. It has 12,360 IBM Power X Cell 8i CPUs. And also 6,480 AMD Opteron dual-core processors. It has a power of 2.35 MW. The OS is the Linux red hat enterprise. It has a memory of 103.6 TiB. Furthermore, the cost is around 100 US million dollars.
These are stored in typically housed rooms with high air flow to permit cooling. The purpose of super-computers is to solve massive problems. Those problems are impossible to solve using standard computers. Features of super computers are is has a large storage capacity. It also has a very fast capability of input output. Linux and Unix are the common OS used in super computers.
Towards Cluster Computing…
What is Cluster Computing?
Cluster Computing is a set of connected computers which works together to form a single computer. The components of each computer are most common. Furthermore, they are connected to a fast local area network to improve the speed of the connection. The purpose of clustering computers is to improve performance. They can work as a single computer. It is cost effective too.
A cluster is consists of nodes, network, operating system, and cluster middleware. The node consists of the master and the other computing nodes.
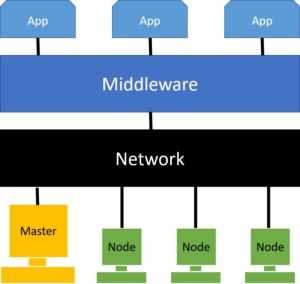
Why we use Cluster Computing?
There are a few factors as reasons to use Cluster Computers. Here are they
- The Bandwidth of Communication: The bandwidth increases because the network is created using the newest technologies and protocols which are implemented in LAN and WANs.
- Easy Integration: More than special parallel computers, workstation clusters are much easier to connect and integrate to currently implemented networks. So that you don’t have to invest in a completely new network.
- The Development tools: The tools and software for cluster computer workstations are more stable than individual solutions.
- Inexpensive: Clustering is inexpensive and already available to work as a high-performance computer at any given time
- Distributed Resources: Since the network is distributed, the resources are distributed too. SO the cost is used effectively.
The motivation for using clusters
- The CPU cycle utilization is less than 10 percent in a desktop workstation
- Rapid improvement of pc and workstation performance
- When the performance is growing the percent utilization is decreased drastically
- Supercomputers are too expensive and organizations reluctant to buy those. And super computers have a much shorter life span. So the best investment is a cluster computer network.
What is computer stealing in Cluster Computing
Cluster Computing, cycle stealing is done to use the RAM and the storage of a workstation without any interference of the CPU. In simple terms stealing RAM and storage without CPU knowing about it. But usually, a node or a workstation is owning by an individual person. It is also allocated to a group or a department. So these have privacy and the usage is only by the owners. When creating a cluster, the workstations are connected and run distributed applications. Then the problem occurs.
There are 3 types of owners users the workstations. And any user can be divided into one of these categories.
- 1: only do document-related activities and sending receiving emails
- 2: Use and work with software development activities including editing, debugging, testing
- 3: Run computer-intensive software and other applications
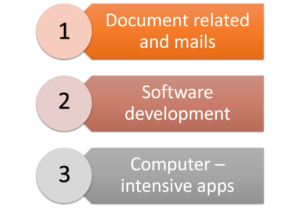
So the cluster is specially designed to steal the spare cycles from the 3 types of users. This has special permissions to gain especially from the users and the organizations. the name for this the ownership hurdle. And overcoming that is main in cycle stealing. And in clusters, this is doing mainly after standard working hours. Because stealing not using cycles are much harder without interfering the CPU in working hours.
Computer food chain
As you all know about the food chain, it usually happens in a hierarchical order. A smaller animal is eaten by a larger animal. And that animal is eaten by another animal who is larger than the larger animal. Then that animal is eaten by the largest of them all. This pattern was also followed in the computer food chain.
In 1984, the computer chain was explained like this. As the smaller animals PC and workstations were identified. Then for larger animals, mini computers and vectors were uses. Then as the largest mainframe computers are used.
Furthermore, in 1994, computer food chain was consist of this. Pc and workstations were considered as smaller animals. And MPP and mini computers are categorized as larger computers. And vector computers and mainframes were considered as the largest. But the mainframes was coming to the end of an era. Whereas, vector computers future was also bleak.
But the current and the future computer food chain is completely different. The nodes, workstations are gathered together and act as the largest computer. They are individual units work together. So they are able to beat the super computers and mainframes. They have higher performance and speed more than the others.
Conclusion,
Cluster computing theory is using workstations and nodes and interconnecting them to work as a single unit. This includes integrating computer resources and the network. they are faster, closer connecting. Low latency and has a looser connection than others. Also, are cost-effective and cheaper when comparing with super computers. In this article we discussed more details on why we are using clusters, motivational factors too. We discussed cycle stealing and about types of users too. Furthermore about the computer food chain and the purpose of it. I hope you got a good understanding of the basics of cluster computing in this article.
